





测绘学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 385-396.doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2025.20240039
• 地图学与地理信息 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-01-21
出版日期:2025-03-11
发布日期:2025-03-11
通讯作者:
黄丽娜
E-mail:liusongwen@whu.edu.cn;linahuang@whu.edu.cn
作者简介:刘嵩雯(1999—),女,硕士生,研究方向为地理空间认知。 E-mail:liusongwen@whu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Songwen LIU1,2( ), Lina HUANG1,2,3(
), Lina HUANG1,2,3( )
)
Received:2024-01-21
Online:2025-03-11
Published:2025-03-11
Contact:
Lina HUANG
E-mail:liusongwen@whu.edu.cn;linahuang@whu.edu.cn
About author:LIU Songwen (1999—), female, postgraduate, majors in geospatial cognition. E-mail: liusongwen@whu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
随着混合现实技术的发展,虚实融合地图应运而生。现有的虚实融合地图广泛使用动态符号,但尚缺乏面向用户认知的动态符号可用性研究,符号参数的适应性也有待验证。本文以应急导航为应用情景,提出虚实融合的动态符号设计方法,采用眼动跟踪技术开展视觉认知试验,分别从符号的静止与运动模态,旋转、跳跃和缩放变化效果,变化速度分级参数3个层次探究动态符号配置的适宜策略。试验结果表明,动态符号可获得与静态符号相仿的认知效果;在符号动态旋转、跳跃和缩放3种变化方式中,缩放效果在信息处理和视觉搜索比较中表现较好;动态符号的变化分级中,选择2~4个等级较合适,随着分级数目的增加,人们识别、加工处理、记忆符号的难度显著增加。
中图分类号:
刘嵩雯, 黄丽娜. 面向虚实融合的应急导航符号动态参量配置及其认知工效分析[J]. 测绘学报, 2025, 54(2): 385-396.
Songwen LIU, Lina HUANG. Dynamic parameter configuration of emergency navigation symbols for virtual-real fusion and its cognitive ergonomics analysis[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2025, 54(2): 385-396.
表1
动态符号的视觉描述参量"
| 动态参量 | 视觉效果 | 表达功效 |
|---|---|---|
| 时长:符号某种状态存续的时间段 | 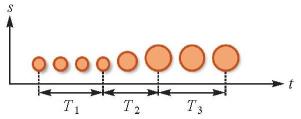 | 描述动态现象的持续过程,或与色相、大小等静态参量组合突出数量和质量特征 |
| 时速:符号状态改变的速度 | 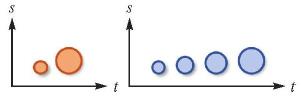 | 描述变化现象的运动过程,或通过闪烁强调静态特征的空间定位或凸显重要性 |
| 时序:符号状态改变过程中的先后次序 | 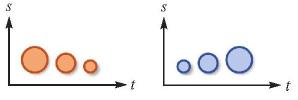 | 表达有序量的出现顺序,升序变化对应特征增强,降序表示特征减弱,或类比于二维空间中的前后关系 |
| 节奏:符号变化的周期性特征 | 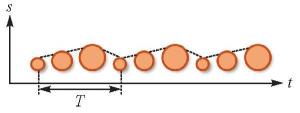 | 描述重复性的动态现象,或通过周期(频率)和振幅表示静态特征的重要程度、等级等性质 |
| 时刻:符号出现、消失或变化的某一时间点 | 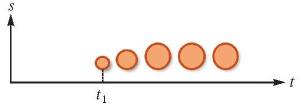 | 对应于动画的关键帧,描述地理事物/现象在某时间点的状态和属性 |
| 同步:两个或多个符号在同一个过程中各自变化 | 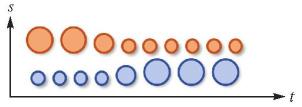 | 描述不同的事物或属性特征同向、逆向或彼此关联的时态变化,即建立动态变化之间的映射关系 |
表4
指标体系"
| 类别 | 指标 | 单位 | 指标解释 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 信息处理 | 首次进入AOI | 无 | 根据首次到达AOI之前所花时间进行赋值,用于评价不同等级符号对被试的视觉吸引;数值越大,被试越容易关注到等级高的符号 |
| AOI总注视时长 | ms | 眼睛在AOI内停留的总时长,用于评价被试解译信息、记忆的过程;总注视时长越长,被试处理AOI信息的时间成本越大[ | |
| AOI注视次数 | 次 | 眼睛在AOI内停留注视的次数,用于评价被试处理的视觉信息;注视次数越多,被试处理的视觉信息越多(但不一定有用)[ | |
| 视觉搜索比较 | 扫视次数 | 次 | 眼睛在注视目标之间快速跳动的次数,用于评价被试在试验中进行视觉搜索和比较的次数。扫视次数越多,被试进行的视觉搜索比较越多[ |
| 认知负担 | 瞳孔扩张 | 无 | 试验任务中瞳孔扩张程度,由试验期间瞳孔最大直径/瞳孔平均直径得到,用于评价被试在试验中的认知负担;瞳孔扩张越大,认知负担越大[ |
表6
3种变化方式的多独立样本的非参数检验"
| 类别 | 指标 | 运动方式 | M±SD | Kruskal-Wallis检验统计量H值 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 信息处理 | 首次进入AOI | 旋转 | 1.033±0.974 | 2.341 | 0.310 |
| 跳跃 | 1.183±0.873 | ||||
| 缩放 | 0.933±0.861 | ||||
| AOI总注视时长/ms | 旋转 | 557.239±665.116 | 5.289 | 0.071 | |
| 跳跃 | 544.704±539.226 | ||||
| 缩放 | 346.664±396.946 | ||||
| AOI注视次数/次 | 旋转 | 1.129±1.016 | 6.941 | 0.031* | |
| 跳跃 | 1.639±1.365 | ||||
| 缩放 | 1.100±1.251 | ||||
| 视觉搜索比较 | 扫视次数/次 | 旋转 | 9.675±3.720 | 22.568 | 0.000* |
| 跳跃 | 8.333±5.514 | ||||
| 缩放 | 5.917±4.040 | ||||
| 认知负担 | 瞳孔扩张 | 旋转 | 1.089±0.036 | 9.534 | 0.009* |
| 跳跃 | 1.116±0.052 | ||||
| 缩放 | 1.100±0.041 |
| [1] | LIN Jing, CAO Lijun, LI Nan. Assessing the influence of repeated exposures and mental stress on human wayfinding performance in indoor environments using virtual reality technology[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2019, 39: 53-61. |
| [2] |
郭仁忠, 陈业滨, 马丁, 等. 论ICT时代的泛地图表达[J]. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(7): 1108-1113. DOI:.
doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20220140 |
|
GUO Renzhong, CHEN Yebin, MA Ding, et al. Pan-map representation in ICT era[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2022, 51(7): 1108-1113. DOI:.
doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20220140 |
|
| [3] | DENG Chen, YOU Xiong, ZHANG Weiwei, et al. A vision-aided localization and geo-registration method for urban ARGIS based on 2D maps[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geoinformation Science, 2022, 5(3): 93-110. |
| [4] | MENG Liqiu. Proliferation of cartographic education in the age of big data[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geoinformation Science, 2022, 5(3): 7-18. |
| [5] | YOO S J, CHOI S H. Indoor AR navigation and emergency evacuation system based on machine learning and IoT technologies[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 9(21): 20853-20868. |
| [6] | CAMPOS A, CORREIA N, ROMÃO T, et al. Mobile augmented reality techniques for emergency response[C]//Proceedings of the 16th EAI International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking and Services. Houston: ACM Press, 2020: 31-39. |
| [7] | 刘兵, 孟立秋. 扩展现实与地理空间认知研究进展与展望[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2022, 47(12): 2047-2053. |
| LIU Bing, MENG Liqiu. Research progress and prospect of extended reality and geospatial cognition[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2022, 47(12): 2047-2053. | |
| [8] | CATAL C, AKBULUT A, TUNALI B, et al. Evaluation of augmented reality technology for the design of an evacuation training game[J]. Virtual Reality, 2020, 24(3): 359-368. |
| [9] | QIU X, WEN L, WU C, et al. Impact of learning methods on spatial knowledge acquisition[J]. Frontiers in Psychology, 2020, 11: 1322. |
| [10] | LIU Bing, DING Linfang, MENG Liqiu. Spatial knowledge acquisition with virtual semantic landmarks in mixed reality-based indoor navigation[J]. Cartography and Geographic Information Science, 2021, 48(4): 305-319. |
| [11] | 张国永, 龚建华, 张冬. 增强现实地图载体的空间认知负荷特征研究[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2024, 26(1): 99-109. |
| ZHANG Guoyong, GONG Jianhua, ZHANG Dong. Research on spatial cognitive load characteristics of augmented reality maps on different carriers[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2024, 26(1): 99-109. | |
| [12] |
龚建华, 李文航, 张国永, 等. 增强地理环境中过程可视化方法:以人群疏散模拟为例[J]. 测绘学报, 2018, 47(8): 1089-1097. DOI:.
doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2018.20180111 |
|
GONG Jianhua, LI Wenhang, ZHANG Guoyong, et al. An augmented geographic environment for geo-process visualization: a case of crowd evacuation simulation[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2018, 47(8): 1089-1097. DOI:.
doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2018.20180111 |
|
| [13] | GRASSET R, LANGLOTZ T, KALKOFEN D, et al. Image-driven view management for augmented reality browsers[C]//Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality. Atlanta: IEEE, 2012: 177-186. |
| [14] | GOMES J V P, DELAZARI L S, SCHMIDT M A R. Evaluating distances using pictorial symbols in augmented reality systems for indoor environments[J]. Abstracts of the ICA, 2021, 3: 1-2. |
| [15] | HALIK Ł, MEDYŃSKA-GULIJ B. The differentiation of point symbols using selected visual variables in the mobile augmented reality system[J]. The Cartographic Journal, 2017, 54(2): 147-156. |
| [16] | 陈嬿, 张琼文, 王嘉琪, 等. 地图符号与情绪效价对AR地图用户空间记忆的影响研究[J]. 图学学报, 2023, 44(2): 399-407. |
| CHEN Yan, ZHANG Qiongwen, WANG Jiaqi, et al. Effects of map symbols and emotional valence on AR map users' spatial memory[J]. Journal of Graphics, 2023, 44(2): 399-407. | |
| [17] | 艾廷华. 动态符号与动态地图[J]. 武汉测绘科技大学学报, 1998, 23(1): 47-51. |
| AI Tinghua. Dynamic symbol and dynamic map[J]. Journal of Wuhan Technical University of Surveying and Mapping, 1998, 23(1): 47-51. | |
| [18] | KRAAK M J. Cartography and the use of animation[M]//Multimedia cartography. Berlin: Springer, 2007: 317-326. |
| [19] | AMORIM F R, SCHMIDT M A R. Classification of dynamic cartographic symbols applied to augmented reality(AR) systems[J]. Proceedings of the ICA, 2021, 4: 1-8. |
| [20] | 李蒙. 自然灾害应急专题图设计与制作方法研究[D]. 郑州: 信息工程大学, 2013. |
| LI Meng. Research on design and manufacturing methods of nature disaster emergency thematic map[D]. Zhengzhou: Information Engineering University, 2013. | |
| [21] | DIBIASE D, MACEACHREN A M, KRYGIER J B, et al. Animation and the role of map design in scientific visualization[J]. Cartography and Geographic Information Systems, 1992, 19(4): 201-214. |
| [22] | MAC E. Time as a cartographic variable[J]. Visualization in Geographical Information Systems, 1994, 243: 115-130. |
| [23] | 付乐宜, 艾廷华, 黄丽娜, 等. 基于交通轨迹数据的三维动态噪声地图[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2020, 22(9): 1789-1798. |
| FU Leyi, AI Tinghua, HUANG Lina, et al. Three-dimensional dynamic noise map based on traffic trajectory data[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2020, 22(9): 1789-1798. | |
| [24] | BERTIN J. Graphics and graphic information-processing[M]. Berlin: De Gruyter, 1981: 186-187. |
| [25] | 杨志坚. 基于混合现实的室内火灾场景可视化及交互关键技术研究[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2019. |
| YANG Zhijian. Research on key technologies of interactive design and visualization of fire scene based on mixed reality[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2019. | |
| [26] | 祝国瑞, 徐智勇, 吴小芳. 基于多重变换组合的动态地图符号设计[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2006, 31(6): 548-551. |
| ZHU Guorui, XU Zhiyong, WU Xiaofang. Design of dynamic map symbol based on multi-transform assembly[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2006, 31(6): 548-551. | |
| [27] | 解智强, 杜清运, 陈厚元, 等. 论地图语言中的动态符号设计与表达[J]. 现代测绘, 2012, 35(4): 25-29. |
| XIE Zhiqiang, DU Qingyun, CHEN Houyuan, et al. Design and expression of the dynamic symbol on the map language[J]. Modern Surveying and Mapping, 2012, 35(4): 25-29. | |
| [28] | 消防安全标志:GB 13495.1—2015[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015. |
| Fire safety signs: GB 13495.1—2015[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2015. | |
| [29] |
姚翔宇, 黄丽娜, 于洋. 数字环境下面状要素分级设色的适宜方案分析[J]. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(2): 290-300. DOI:.
doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20200499 |
|
YAO Xiangyu, HUANG Lina, YU Yang. Suitability analysis of graded color schemes for area feature rendering in digital environment[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2022, 51(2): 290-300. DOI:.
doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20200499 |
|
| [30] | GARLANDINI S, FABRIKANT S I. Evaluating the effectiveness and efficiency of visual variables for geographic information visualization[C]//Proceeding of the 9th International Conference on Spatial Information Theory. Berlin: Springer, 2009: 195-211. |
| [31] | BURG A, HULBERT S. Dynamic visual acuity as related to age, sex, and static acuity[J]. Journal of Applied Psychology, 1961, 45(2): 111-116. |
| [32] | MILLER G A. The magical number seven, plus or minus two: some limits on our capacity for processing information[J]. Psychological Review, 1956, 63: 81-97. |
| [33] | CYBULSKI P, WIELEBSKI Ł. Effectiveness of dynamic point symbols in quantitative mapping[J]. The Cartographic Journal, 2019, 56(2): 146-160. |
| [34] | BUCKLEY A. Guidelines for the effective design of spatio-temporal maps[C]//Proceedings of the 26th International Cartographic Conference International Cartographic Association. Dresden: [s.n.], 2013: 1-21. |
| [35] | 朱琳, 王圣凯, 袁伟舜, 等. 眼动控制的交互式地图设计[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2020, 45(5): 736-743. |
| ZHU Lin, WANG Shengkai, YUAN Weishun, et al. An interactive map based on gaze control[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(5): 736-743. | |
| [36] | 李伟, 陈毓芬. 地图学眼动研究及实验参数解析[J]. 测绘通报, 2012(10): 16-20. |
| LI Wei, CHEN Yufen. Cartography eye movements study and the experimental parameters analysis[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2012(10): 16-20. | |
| [37] | LERMAN J. Study design in clinical research: sample size estimation and power analysis[J]. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia, 1996, 43(2): 184-191. |
| [38] | 董卫华, 廖华, 詹智成, 等. 2008年以来地图学眼动与视觉认知研究新进展[J]. 地理学报, 2019, 74(3): 599-614. |
| DONG Weihua, LIAO Hua, ZHAN Zhicheng, et al. New research progress of eye tracking-based map cognition in cartography since 2008[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2019, 74(3): 599-614. |
| [1] | 李华蓉, 郑嘉欣, 李天童. 室内POI显著度评价的Fisher判别法模型[J]. 测绘学报, 2023, 52(4): 679-688. |
| [2] | 李精忠, 毛凯楠. 典型时间规整算法支持下的建筑物形状相似性度量[J]. 测绘学报, 2023, 52(12): 2197-2208. |
| [3] | 郑束蕾. 地理空间认知理论与地图工具的发展[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(6): 766-776. |
| [4] | 晏雄锋, 艾廷华, 杨敏, 郑建滨. 地图空间形状认知的自编码器深度学习方法[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(6): 757-765. |
| [5] | 应申, 张雯博, 苏俊如, 黄丽娜. 地球球观认知分析:以谷歌地球上的寻路任务为例[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(6): 739-748. |
| [6] | 万刚, 武易天. 地图空间认知的数学基础[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(6): 726-738. |
| [7] | 高俊, 曹雪峰. 空间认知推动地图学学科发展的新方向[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(6): 711-725. |
| [8] | 黄丽娜, 张定娆, 应申, 艾廷华. 桌面式虚拟环境与真实环境中个体特征影响空间认知能力的差异分析[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(4): 509-521. |
| [9] | 魏智威, 郭庆胜, 程璐, 刘洋, 童莹. 建筑物图形形状相似性计算的序列分析法[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(12): 1683-1693. |
| [10] | 杜萍, 刘涛, 李鼎凯, 杨晓霞. 应急场景快速制图及地图信息传输[J]. 测绘学报, 2019, 48(6): 747-755. |
| [11] | 王圣音, 刘瑜, 陈泽东, 施力, 张晶. 大众点评数据下的城市场所范围感知方法[J]. 测绘学报, 2018, 47(8): 1105-1113. |
| [12] | 万刚, 曹雪峰. 地理空间信息网格的历史演变与思考[J]. 测绘学报, 2016, 45(S1): 15-22. |
| [13] | 唐炉亮, 刘章, 杨雪, 阚子涵, 李清泉, 董坤. 符合认知规律的时空轨迹融合与路网生成方法[J]. 测绘学报, 2015, 44(11): 1271-1276. |
| [14] | 刘慧敏 邓敏 樊子德 卢启栋. 地图上居民地空间信息的特征度量法[J]. 测绘学报, 2014, 43(10): 1092-1098. |
| [15] | 艾廷华 周梦杰 陈亚婕. 专题地图属性信息的LOD表达与TreeMap可视化[J]. , 2013, 42(3): 0-0. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||