





测绘学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (12): 2262-2275.doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2025.20250162
收稿日期:2025-04-16
修回日期:2025-11-01
出版日期:2026-01-15
发布日期:2026-01-15
通讯作者:
武芳
E-mail:qiuyue@whu.edu.cn;wufang_630@126.com
作者简介:邱越(1997—),男,博士生,研究方向为地理空间数据智能处理。 E-mail:qiuyue@whu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Yue QIU( ), Fang WU(
), Fang WU( ), Renjian ZHAI, Haizhong QIAN, Zhekun HUANG, Bo LI
), Renjian ZHAI, Haizhong QIAN, Zhekun HUANG, Bo LI
Received:2025-04-16
Revised:2025-11-01
Online:2026-01-15
Published:2026-01-15
Contact:
Fang WU
E-mail:qiuyue@whu.edu.cn;wufang_630@126.com
About author:QIU Yue (1997—), male, PhD candidate, majors in intelligent geospatial data processing. E-mail: qiuyue@whu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
多源建筑物矢量数据的精确匹配与融合对城市空间分析与应用至关重要,然而其普遍存在的空间位置不一致性构成了主要技术瓶颈,严重制约匹配精度与数据融合质量。现有空间对齐方法或陷入“先匹配后对齐”的循环依赖困境,无法从根本上改善匹配条件;或采用全局/局部变换模型,难以精细校正实体级非线性偏差,且常因引入几何形变而干扰后续基于形态的匹配判据。针对上述局限,本文提出一种面向匹配优化的多源建筑物实体级保形空间对齐模型,采用“矢量-栅格-矢量”协同工作流,在匹配流程前独立执行:首先,提取建筑物质心构建Delaunay三角网以表征空间结构,并将其栅格化;其次,在栅格域运用全局-局部渐进式特征匹配策略,高效识别高置信度同名点对;然后,基于可靠同名点构建连续精细的位移场,且关键在于,利用该位移场驱动每个源建筑物多边形进行整体刚性平移,在精确校正位置偏差的同时严格保持其固有几何形状;最后,结合拓扑冲突检测与消解机制确保空间有效性。试验结果表明,本文方法显著改善了多源数据的空间一致性,平均Hausdorff距离相对减小18.23%,并使多种下游匹配算法的F1值分别获得1.09至6.65个百分点不等的绝对提升量。试验证实了本文方法作为一种高效的预处理策略,在提升多源建筑物矢量数据匹配精度与融合质量方面的有效性与应用潜力。
中图分类号:
邱越, 武芳, 翟仁健, 钱海忠, 黄哲琨, 李博. 面向匹配优化的多源建筑物实体级保形空间对齐模型[J]. 测绘学报, 2025, 54(12): 2262-2275.
Yue QIU, Fang WU, Renjian ZHAI, Haizhong QIAN, Zhekun HUANG, Bo LI. An entity-level conformal spatial alignment model for multi-source building matching optimization[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2025, 54(12): 2262-2275.
表1
空间对齐效果栅格域评价指标"
| 指标 | 定义 | 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 互信息(MI) | MI(A,B)=H(A)+H(B)-H(A,B) | H(•)为信息熵,A、B为标准化后的栅格图像 | 度量信息共享程度,值越大表明分布协同性越强 |
| 均方误差(MSE) | 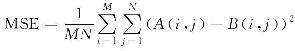 | M、N为图像尺寸 | 直接反映像素级差异,值越小表明对齐精度越高 |
| 峰值信噪比(PSNR) | 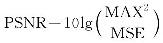 | MAX为图像最大值 | 对数尺度敏感度指标,值越大表明对齐质量越高 |
| 结构相似性指数(SSIM) | 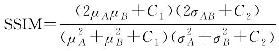 | μ为均值,σ为方差,C1、C2均为稳定性常数 | 综合亮度、对比度、结构相似性,越接近1越好 |
| 归一化互相关(NCC) | 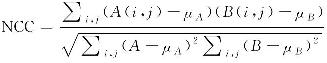 | μA、μB均为图像均值 | 衡量线性相关性,值越接近1表明分布模式越相似 |
| Dice系数 | 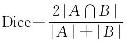 |  | 量化空间重叠度,值越接近1表明重叠区域越大 |
表4
不同空间对齐方法的性能对比"
| 指标 | 对齐前 | 本文方法 | 人工标记1对 | 人工标记5对 | 人工标记9对 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对齐后 | 相对提升量/(%) | 对齐后 | 相对提升量/(%) | 对齐后 | 相对提升量/(%) | 对齐后 | 相对提升量/(%) | ||
| MSE | 0.149 9 | 0.116 7 | 22.15 | 0.151 0 | -0.73 | 0.141 3 | 5.74 | 0.136 4 | 9.01 |
| NCC | 0.545 9 | 0.647 6 | 18.63 | 0.542 9 | -0.55 | 0.574 0 | 5.15 | 0.588 4 | 7.79 |
| PSNR | 8.240 9 | 9.327 9 | 13.19 | 8.210 8 | -0.37 | 8.498 9 | 3.13 | 8.652 0 | 4.99 |
| MI | 0.184 6 | 0.261 3 | 41.55 | 0.182 5 | -1.14 | 0.204 6 | 10.83 | 0.214 9 | 16.41 |
| SSIM | 0.779 3 | 0.816 0 | 4.71 | 0.778 4 | -0.12 | 0.788 8 | 1.22 | 0.793 8 | 1.86 |
| DICE | 0.640 5 | 0.721 2 | 12.60 | 0.638 1 | -0.37 | 0.663 3 | 3.56 | 0.674 5 | 5.31 |
| Hausdorff | 100.121 4 | 88.763 0 | 11.34 | 88.206 1 | 11.90 | 87.080 3 | 13.03 | 87.080 3 | 13.03 |
| 平均Hausdorff | 8.660 2 | 7.081 6 | 18.23 | 8.415 0 | 2.83 | 8.505 4 | 1.79 | 7.990 5 | 7.73 |
表6
不同空间对齐方法对匹配性能提升的对比"
| 匹配方法 | 查准率绝对提升量 | 查全率绝对提升量 | F1值绝对提升量 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 人工-1 | 人工-5 | 人工-9 | 本文方法 | 人工-1 | 人工-5 | 人工-9 | 本文方法 | 人工-1 | 人工-5 | 人工-9 | 本文方法 | |
| 位置法 | -8.02 | -2.69 | 2.37 | 6.43 | -7.12 | -1.10 | 1.64 | 5.47 | -7.81 | -2.12 | 2.12 | 6.13 |
| 重叠法 | -7.93 | 2.11 | 2.78 | 8.09 | -4.56 | 4.20 | 2.01 | 4.75 | -6.60 | 3.00 | 2.46 | 6.65 |
| 3指标法 | -0.22 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 1.79 | -2.37 | -1.28 | -1.64 | 0.18 | -1.16 | -0.27 | -0.55 | 1.09 |
| 6指标法 | -6.72 | 4.39 | 3.80 | 6.86 | -5.83 | 4.02 | 2.56 | 5.84 | -6.45 | 4.28 | 3.33 | 6.51 |
| [1] | 武芳, 王泽根, 蔡忠亮, 等. 空间数据库原理[M]. 武汉: 武汉大学出版社, 2017: 230-231. |
| WU Fang, WANG Zegen, CAI Zhongliang, et al. Spatial database principle[M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University Press, 2017: 230-231. | |
| [2] | 杨飞, 华一新, 李响, 等. 基于多粒度时空对象数据模型的城市基础设施建模与管理[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2021, 23(11): 1984-1997. |
| YANG Fei, HUA Yixin, LI Xiang, et al. An urban facilities modeling and management method based on the multi-granularity spatiotemporal object data model[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2021, 23(11): 1984-1997. | |
| [3] | 张新长, 华淑贞, 齐霁, 等. 新型智慧城市建设与展望:基于AI的大数据、大模型与大算力[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2024, 26(4): 779-789. |
| ZHANG Xinchang, HUA Shuzhen, QI Ji, et al. Progress and prospects of new smart city construction: AI-based big data, big models and big computing power[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2024, 26(4): 779-789. | |
| [4] |
张永军, 张祖勋, 龚健雅. 天空地多源遥感数据的广义摄影测量学[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(1): 1-11. DOI: .
doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2021.20200245 |
|
ZHANG Yongjun, ZHANG Zuxun, GONG Jianya. Generalized photogrammetry of spaceborne, airborne and terrestrial multi-source remote sensing datasets[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2021, 50(1): 1-11. DOI: .
doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2021.20200245 |
|
| [5] | 李德仁. 新基建时代地理信息产业的机遇与挑战[J]. 中国工业和信息化, 2020(12): 52-57. |
| LI Deren. Opportunities and challenges of geographic information industry in the new infrastructure era[J]. China Industry & Information Technology, 2020(12): 52-57. | |
| [6] | 杨明旺, 赵丽科, 叶林峰, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的遥感影像建筑物提取方法综述[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2024, 26(6): 1500-1516. |
| YANG Mingwang, ZHAO Like, YE Linfeng, et al. A review of convolutional neural networks related methods for building extraction from remote sensing images[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2024, 26(6): 1500-1516. | |
| [7] | DOYTSHER Y. A rubber sheeting algorithm for non-rectangular maps[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2000, 26(9/10): 1001-1010. |
| [8] | WEI R, MURRAY A T. An integrated approach for addressing geographic uncertainty in spatial optimization[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2012, 26(7): 1231-1249. |
| [9] | 赵东保, 盛业华, 张卡. 利用几何矩和叠置分析进行多尺度面要素自动匹配[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2011, 36(11): 1371-1375. |
| ZHAO Dongbao, SHENG Yehua, ZHANG Ka. An algorithm for muti-scale one-to-many areal feature matching based on geometry moments and overly analysis[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2011, 36(11): 1371-1375. | |
| [10] | 刘凌佳. 多尺度面实体匹配方法及其融合应用研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2018. |
| LIU Lingjia. Research on methods and integration applications of polygonal object matching on multi-scale datasets[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2018. | |
| [11] | CHEN S, SHI W, ZHOU M, et al. CDasXORNet: change detection of buildings from bi-temporal remote sensing images as an XOR problem[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2024, 130(1): 103836. |
| [12] | TONG Xiaohua, LIANG Dan, JIN Yanmin. A linear road object matching method for conflation based on optimization and logistic regression[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2014, 28(4): 824-846. |
| [13] | WANG Yanxia, CHEN Deng, ZHAO Zhiyuan, et al. A back-propagation neural network-based approach for multi-represented feature matching in update propagation[J]. Transactions in GIS, 2015, 19(6): 964-993. |
| [14] | 李德仁, 龚健雅, 张桥平. 论地图数据库合并技术[J]. 测绘科学, 2004, 29(1): 1-4. |
| LI Deren, GONG Jianya, ZHANG Qiaoping. On the conflation of geographic databases[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2004, 29(1): 1-4. | |
| [15] |
张新长, 何显锦, 孙颖, 等. 多尺度空间数据联动更新技术研究现状及展望[J]. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(7): 1520-1535. DOI: .
doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20220095 |
|
ZHANG Xinchang, HE Xianjin, SUN Ying, et al. Advance and future development of the multi-scale spatial data linkage updating[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2022, 51(7): 1520-1535. DOI: .
doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20220095 |
|
| [16] | SCHORCHT M, HECHT R, MEINEL G. Comparative study on matching methods for the distinction of building modifications and replacements based on multi-temporal building footprint data[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2022, 11(2): 91-107. |
| [17] | DUAN Weiwei, CHIANG Yaoyi, LEYK S, et al. Automatic alignment of contemporary vector data and georeferenced historical maps using reinforcement learning[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2020, 34(4): 824-849. |
| [18] | 翟仁健. 基于全局一致性评价的多尺度矢量空间数据匹配方法研究[D]. 郑州: 信息工程大学, 2011. |
| ZHAI Renjian. Research on automated matching methods for multi-scale vector spatial data based on global consistency evaluation[D]. Zhengzhou: Information Engineering University, 2011. | |
| [19] | 蓝振家. 顾及邻域相似性的面实体匹配最优化方法[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2019. |
| LAN Zhenjia. Optimization method for areal feature matching considering context-dependent similarity[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2019. | |
| [20] | 朱欣焰, 刘凌佳. 一种用于空间数据整合的建筑物面实体对齐方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2018, 43(12): 2269-2277. |
| ZHU Xinyan, LIU Lingjia. A building polygonal object alignment approach for spatial data integration[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2018, 43(12): 2269-2277. | |
| [21] | 张付兵, 温伯威, 郭丽萍, 等. 基于机器学习的多源矢量同名面实体几何不一致性识别和处理方法[J]. 测绘科学技术学报, 2024, 40(4): 411-417. |
| ZHANG Fubing, WEN Bowei, GUO Liping, et al. A method for recognizing and processing geometric inconsistencies in multi-source identical polygonal vector entities based on machine learning[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2024, 40(4): 411-417. | |
| [22] | KOVALERCHUK B, DOUCETTE P, SEEDAHMED G, et al. Automated vector-to-raster image registration[C]//Proceedings of 2008 Algorithms and Technologies for Multispectral, Hyperspectral, and Ultraspectral Imagery XIV. Orlando: SPIE, 2008: 69660W. |
| [23] | 杜永葛, 霍亮, 程宏宇, 等. 矢量数据校正工具集的设计与实现[J]. 矿山测量, 2017, 45(1): 9-13. |
| DU Yongge, HUO Liang, CHENG Hongyu, et al. Design and implementation of vector data correction toolkit[J]. Mine Survey, 2017, 45(1): 9-13. | |
| [24] | 王艳东, 邵鑫, 刘波, 等. 一种利用Mask R-CNN的遥感影像与矢量数据配准方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2022, 47(4): 623-631. |
| WANG Yandong, SHAO Xin, LIU Bo, et al. A registration method of remote sensing image and vector data using mask R-CNN[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2022, 47(4): 623-631. | |
| [25] | RUIZ-LENDÍNEZ J J, MAĆKIEWICZ B, MOTEK P, et al. Method for an automatic alignment of imagery and vector data applied to cadastral information in Poland[J]. Survey Review, 2019, 51(365): 123-134. |
| [26] | YUAN Lang, LI Yuxia, YANG Chao, et al. Road vectorization based on image pixel tracking and attribute matching method[C]//Proceedings of 2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Waikoloa: IEEE, 2020: 3199-3202. |
| [27] | FAN Hongchao, ZIPF A, FU Qing, et al. Quality assessment for building footprints data on OpenStreetMap[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2014, 28(4): 700-719. |
| [28] | 郝燕玲, 唐文静, 赵玉新, 等. 基于空间相似性的面实体匹配算法研究[J]. 测绘学报, 2008, 37(4): 501-506. |
| HAO Yanling, TANG Wenjing, ZHAO Yuxin, et al. Areal feature matching algorithm based on spatial similarity[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2008, 37(4): 501-506. | |
| [29] | 汪汇兵, 唐新明, 邱博, 等. 运用多算子加权的面要素几何匹配方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2013, 38(10): 1243-1247. |
| WANG Huibing, TANG Xinming, QIU Bo, et al. Geometric matching method of area feature based on multi-weighted operators[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2013, 38(10): 1243-1247. | |
| [30] | LIU Lingjia, DING Xiaohui, ZHU Xinyan, et al. An iterative approach based on contextual information for matching multi-scale polygonal object datasets[J]. Transactions in GIS, 2020, 24(4): 1047-1072. |
| [31] | 郭黎, 崔铁军, 郑海鹰, 等. 基于空间方向相似性的面状矢量空间数据匹配算法[J]. 测绘科学技术学报, 2008(5): 380-382. |
| GUO Li, CUI Tiejun, ZHENG Haiying, et al. Arithmetic for area vector spatial data matching on spatial direction similarity[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2008(5): 380-382. | |
| [32] | 邵世维. 基于几何特征的多尺度矢量面状实体匹配方法研究与应用[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2012. |
| SHAO Shiwei. Researches and applications on polygon entity matching for multi-scale vector data based on geometric features[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2012. | |
| [33] | POTJE G, CADAR F, ARAUJO A, et al. XFeat: accelerated features for lightweight image matching[C]//Proceedings of 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle: IEEE, 2024: 2682-2691. |
| [34] | LOWE D G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features[C]//Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Kerkyra: IEEE, 1999: 1150-1157. |
| [35] | BAY H, TUYTELAARS T, VAN GOOL L. SURF: speeded up robust features[M]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2006. Berlin: Springer, 2006: 404-417. |
| [36] | RUBLEE E, RABAUD V, KONOLIGE K, et al. ORB: an efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF[C]//Proceedings of 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision. Barcelona: IEEE, 2011: 2564-2571. |
| [37] | XU Shibiao, CHEN Shunpeng, XU Rongtao, et al. Local feature matching using deep learning: a survey[J]. Information Fusion, 2024, 107: 102344. |
| [38] | BALAKRISHNAN G, ZHAO A, SABUNCU M R, et al. VoxelMorph: a learning framework for deformable medical image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 38(8): 1788-1800. |
| [39] | MENG Mingyuan, BI Lei, FENG Dagan, et al. Non-iterative coarse-to-fine registration based on single-pass deep cumulative learning[M]//Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention-MICCAI 2022. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2022: 88-97. |
| [40] | MENG Mingyuan, BI Lei, FULHAM M, et al. Non-iterative coarse-to-fine Transformer networks for joint affine and deformable image registration[M]//Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention-MICCAI 2023. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2023: 750-760. |
| [41] | AI Tinghua, ZHANG Xiang, ZHOU Qi, et al. A vector field model to handle the displacement of multiple conflicts in building generalization[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2015, 29(8): 1310-1331. |
| [42] | XU Yongyang, LI Jun, XIE Xuejing, et al. Matching the building footprints of different vector spatial datasets at a similar scale based on one-class support vector machines[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2024, 38(8): 1555-1582. |
| [1] | 刘万增, 王新鹏, 赵婷婷, 翟曦, 李然, 朱秀丽, 蒋志浩, 彭云璐, 张晔. 碎片化地形矢量数据比例尺评估方法[J]. 测绘学报, 2024, 53(6): 1013-1024. |
| [2] | 李皓, 乐鹏, 姜良存, 张明达, 梁哲恒. 矢量地理信息溯源记录组织验证的区块链技术[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(6): 823-832. |
| [3] | 谢鹏, 杨春成, 熊顺, 何列松, 周校东. 基于HBase的空间矢量数据存储模型设计与优化[J]. 测绘学报, 2020, 49(10): 1365-1373. |
| [4] | 佟德宇, 朱长青, 任娜. 小数据量矢量地理数据水印算法[J]. 测绘学报, 2018, 47(11): 1518-1525. |
| [5] | 逯跃锋. 基于形状特征的矢量数据与影像数据配准方法研究[J]. 测绘学报, 2014, 43(8): 879-879. |
| [6] | 马小龙 李成名 赵占杰. 道路交叉口自动检测与基于OSG的三维自动建模方法[J]. 测绘学报, 2014, 43(10): 1083-1091. |
| [7] | 杨成松,朱长青. 基于常函数的抗几何变换的矢量地理数据水印算法[J]. 测绘学报, 2011, 40(2): 256-261. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||