Salient object detection in remote sensing images (SOD) effectively distinguishes key features and regions within images, thus enhancing the precision and efficiency of image analysis. However, due to the complexity of remote sensing images, existing remote sensing images SOD methods suffer from issues such as inaccurate target localization, blurred boundaries, and weak target confidence. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a novel method for remote sensing images SOD that integrates edge and global information. Initially, an edge feature enhancement module is designed, utilizing the Sobel operator to extract edge information from shallow feature maps to generate boundary clue feature maps. These are integrated with boundary attention and spatial-channel attention to further enhance local feature representation, effectively mitigating the issue of blurred salient object boundaries. Secondly, a global context feature enhancement module is introduced, acquiring image-level semantic information through global average pooling and fully connected layers, and combining it with spatial attention mechanisms to generate global association maps. Based on this, the multi-scale attention and context feature enhancement strategies are employed to improve the confidence and localization accuracy of salient objects. Finally, to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, this paper conducted experimental analysis on three ORSSD datasets, the EORSSD dataset, and the ORSI4199 dataset. The 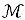 scores decreased by 0.001 3~0.120 5, 0.001~0.159 3, and 0.003 5~0.136 7, respectively. The Sα scores increased by 0.005 7~0.266 3, 0.003~0.336 6, and 0.013 9~0.240 3, respectively. The Fβ scores increased by 0.031 4~0.339 1, 0.023 2~0.517 8, and 0.004 3~0.328 9, respectively. The results demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms existing methods in detection accuracy and efficiency, effectively handling complex scenes and variable conditions in remote sensing images.
scores decreased by 0.001 3~0.120 5, 0.001~0.159 3, and 0.003 5~0.136 7, respectively. The Sα scores increased by 0.005 7~0.266 3, 0.003~0.336 6, and 0.013 9~0.240 3, respectively. The Fβ scores increased by 0.031 4~0.339 1, 0.023 2~0.517 8, and 0.004 3~0.328 9, respectively. The results demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms existing methods in detection accuracy and efficiency, effectively handling complex scenes and variable conditions in remote sensing images.



